The Eulerian transport model simulates the transport, dispersion and decay of dissolved or suspended substances under the influence of the water currents. The Eulerian transport model can be coupled with SLIM1D, SLIM2D or SLIM3D to simulate a wide range of hydrodynamic phenomena in rivers, lake, estuaries, coastal seas and in the deep ocean. The tracer diffusivities can be calculated with state-of-the-art turbulence models. The transport equation is discretised with the Discontinuous Galerkin finite element method, which ensures optimal accuracy even for advection-dominated processes.
Tracers that can be modelled include bacteria, radioactive elements, flow diagnostics such as the water age, temperature, salinity and fine-grained sediments. The latter can simulated with SLIM2D and SLIM3D. In a 3D simulation, a vertical sediment settling velocity is added to the hydrodynamical vertical velocity. This velocity is proportional to the sediment concentration, as it is characteristic of cohesive sediment. The sediment plume is then much smaller than the freshwater plume.
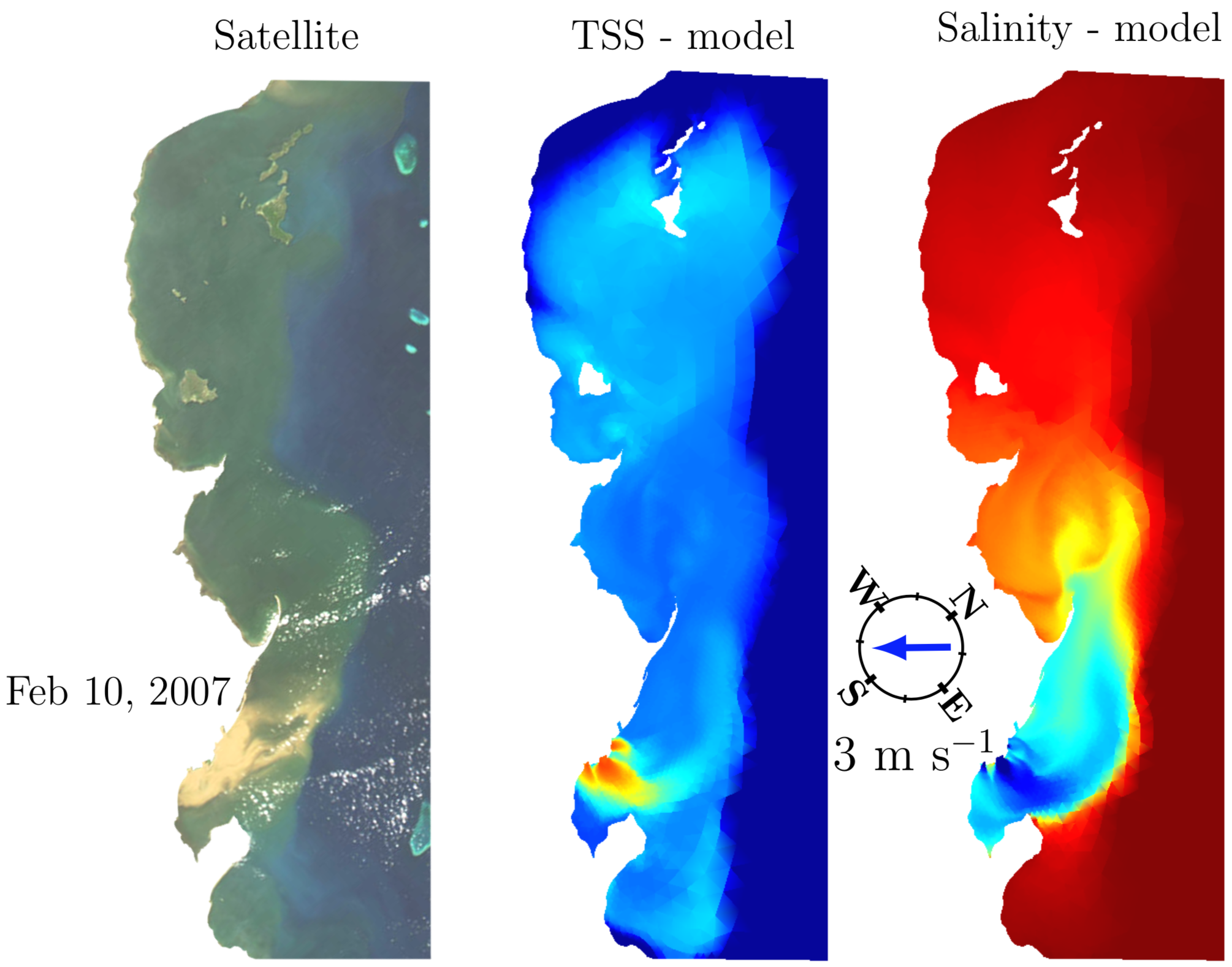
Sediment and freshwater plumes as modeled by SLIM3D and the Eulerian transport model in the Burdekine River (Australia). To learn more…
778265
tracers
1
apa
50
date
desc
7113
https://www.slim-ocean.be/wp-content/plugins/zotpress/
%7B%22status%22%3A%22success%22%2C%22updateneeded%22%3Afalse%2C%22instance%22%3Afalse%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22request_last%22%3A0%2C%22request_next%22%3A0%2C%22used_cache%22%3Atrue%7D%2C%22data%22%3A%5B%7B%22key%22%3A%22V6TLSQ66%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Purkis%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222023-03-31%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPurkis%2C%20S.%20J.%2C%20Oehlert%2C%20A.%20M.%2C%20Dobbelaere%2C%20T.%2C%20Hanert%2C%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Harris%2C%20P.%20%28Mitch%29.%20%282023%29.%20Always%20a%20White%20Christmas%20in%20the%20Bahamas%3A%20temperature%20and%20hydrodynamics%20localize%20winter%20mud%20production%20on%20Great%20Bahama%20Bank.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BJournal%20of%20Sedimentary%20Research%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B93%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%283%29%2C%20145%26%23x2013%3B160.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.2110%5C%2Fjsr.2022.066%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.2110%5C%2Fjsr.2022.066%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Always%20a%20White%20Christmas%20in%20the%20Bahamas%3A%20temperature%20and%20hydrodynamics%20localize%20winter%20mud%20production%20on%20Great%20Bahama%20Bank%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sam%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Purkis%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Amanda%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Oehlert%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Thomas%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dobbelaere%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Emmanuel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hanert%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Paul%20%28Mitch%29%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Harris%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Whitings%2C%20or%20occurrences%20of%20%5Cufb01ne-grained%20carbonate%20in%20the%20water%20column%2C%20have%20been%20observed%20in%20modern%20environments%20with%20salinities%20ranging%20from%20fresh%20to%20marine%20conditions%2C%20and%20thick%20deposits%20of%20lime%20mud%20are%20described%20throughout%20the%20geological%20record.%20Despite%20their%20ubiquity%2C%20the%20trigger%20for%20whitings%20has%20been%20debated%20for%20more%20than%20eighty%20years.%20Satellite%20data%20reveal%20that%20most%20whitings%20are%20restricted%20to%20the%20northwestern%20part%20of%20Great%20Bahama%20Bank%20%28GBB%29%20which%20occupies%20%2C%2010%25%20of%20the%20platform%20area.%20Even%20here%2C%20whitings%20are%20further%20focused.%20More%20than%2035%25%20of%20them%20occur%20in%20a%20zone%20which%20occupies%20just%201%25%20of%20the%20platform.%20We%20propose%20a%20three-step%20process%20for%20the%20existence%20of%20this%20zone%20of%20peak%20whitings%20and%20why%20the%20whitings%20in%20it%20are%20both%20more%20frequent%20and%20larger%20in%20winter%20than%20summer.%20First%2C%20the%20temperature%20differential%20between%20on-%20and%20off-platform%20waters%20is%20highest%20in%20the%20winter%2C%20setting%20up%20a%20disparity%20between%20dissolved%20CO2%20concentrations%20in%20the%20two%20water%20masses.%20Second%2C%20hydrodynamic%20mixing%20of%20these%20two%20water%20masses%20increases%20the%20degree%20of%20aragonite%20saturation%20of%20the%20platform-top%20waters%2C%20as%20colder%20on-platform%20waters%20with%20theoretically%20higher%20concentrations%20of%20dissolved%20gases%20are%20warmed%20via%20mixing%20with%20the%20warmer%20off-platform%20waters.%20Finally%2C%20spatial%20heterogeneity%20in%20the%20degree%20of%20aragonite%20saturation%20is%20higher%20in%20the%20winter%2C%20and%20the%20zone%20of%20peak%20whitings%20is%20situated%20in%20an%20area%20of%20locally%20enhanced%20saturation%20state.%20Hydrodynamic%20simulation%20suggests%20that%20the%20whitings%20zone%20is%20located%20by%20tidal%20in%5Cufb02ow%20of%20off-platform%20waters%20across%20the%20western%20margin%20of%20GBB%2C%20as%20well%20as%20in%5Cufb02ow%20from%20the%20Tongue%20of%20the%20Ocean%20to%20the%20north%20of%20Andros%20Island.%20Despite%20thermodynamic%20forcing%20mechanisms%20that%20predict%20higher%20frequency%20of%20whitings%20in%20the%20summer%2C%20the%20environmental%2C%20hydrodynamic%2C%20geochemical%2C%20and%20kinetic%20conditions%20in%20the%20whitings%20zone%20appear%20to%20support%20the%20Goldilocks%20con%5Cufb01guration%20that%20enhances%20the%20formation%20of%20wintertime%20whitings%20on%20Great%20Bahama%20Bank.%20This%20phenomenon%20has%20implications%20for%20the%20interpretation%20of%20whitings%20mud%20in%20the%20geological%20record%2C%20including%20the%20geochemical%20signatures%20within%20it.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222023-03-31%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.2110%5C%2Fjsr.2022.066%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%221938-3681%2C%201527-1404%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fpubs.geoscienceworld.org%5C%2Fjsedres%5C%2Farticle%5C%2F93%5C%2F3%5C%2F145%5C%2F620896%5C%2FAlways-a-White-Christmas-in-the-Bahamas%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222023-03-12T19%3A10%3A21Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22PFFJ4E5Q%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Lopez%5Cu2010Gamundi%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222022%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BLopez%26%23x2010%3BGamundi%2C%20C.%2C%20Dobbelaere%2C%20T.%2C%20Hanert%2C%20E.%2C%20Harris%2C%20P.%20M.%2C%20Eberli%2C%20G.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Purkis%2C%20S.%20J.%20%282022%29.%20Simulating%20sedimentation%20on%20the%20Great%20Bahama%20Bank%20%26%23x2013%3B%20Sources%2C%20sinks%20and%20storms.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BSedimentology%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B69%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%287%29%2C%202693%26%23x2013%3B2714.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fsed.13020%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fsed.13020%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Simulating%20sedimentation%20on%20the%20Great%20Bahama%20Bank%20%5Cu2013%20Sources%2C%20sinks%20and%20storms%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Cecilia%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lopez%5Cu2010Gamundi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Thomas%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Dobbelaere%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Emmanuel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hanert%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Paul%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Harris%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Gregor%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Eberli%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sam%20J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Purkis%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22editor%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tracy%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Frank%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22This%20study%20developed%20a%20high-%5Cufb01delity%20hydrodynamic%20simulation%20of%20sediment%20production%2C%20transport%20and%20deposition%20for%20the%20Great%20Bahama%20Bank.%20This%20model%20was%20run%20with%20a%20time-step%20of%2015%20min%20for%20the%20entirety%20of%202016%2C%20forced%20by%20tides%2C%20off-platform%20circulation%20and%20wind.%20Encompassed%20in%20this%20run%20are%20364%20days%20of%20fair-weather%20conditions%20and%20two%20days%20when%20the%20passage%20of%20Category%204%20Matthew%20brought%20hurricane-force%20winds%20to%20the%20platform.%20This%20simulation%20therefore%20offers%20an%20excellent%20opportunity%20to%20contrast%20the%20sway%20of%20fair-weather%20and%20storm-weather%20conditions%20on%20sculpting%20the%20facies%20arrangement%20atop%20this%20100%20000%20km2%20shallow-water%20carbonate%20platform.%20The%20work%20suggests%20that%20fairweather%20conditions%20are%20suf%5Cufb01cient%20to%20deliver%20the%20platform%5Cu2019s%20broad-scale%20facies%20patterns.%20Even%20the%20lethargic%20currents%20of%20the%20platform%20interior%20can%20move%20mud%20%28%26lt%3B63%20%5Cu03bcm%29%20over%20200%20km%20from%20its%20source%20over%20the%20course%20of%20one%20year.%20Intense%20focusing%20of%20tidal%20currents%20between%20islands%20and%20close%20to%20the%20platform%20margin%20are%20ample%20to%20move%20coarse%20grains%20%28%26gt%3B450%20%5Cu03bcm%29%2C%20at%20least%20locally%2C%20as%20is%20necessary%20to%20produce%20the%20vast%20ooid%20fairways%20for%20which%20the%20Great%20Bahama%20Bank%20is%20famed.%20Even%20at%20the%20height%20of%20Hurricane%20Matthew%2C%20average%20current%20speeds%20in%20these%20tidally-dominated%20areas%20do%20not%20exceed%20the%20speeds%20simulated%20for%20fairweather%20conditions.%20Hence%2C%20the%20hurricane%20has%20negligible%20effect%20in%20these%20highenergy%20areas.%20The%20hurricane%20does%20not%20have%20zero%20impact%2C%20though.%20For%20up%20to%20110%20km%20either%20side%20of%20the%20storm%5Cu2019s%20track%2C%20winds%20exceeding%2026%20m%5C%2Fs%20induce%20currents%20that%20winnow%20mud%20over%20longer%20distances%20than%20delivered%20by%20fair-weather%20conditions.%20Hence%2C%20the%20storm%20has%20a%20sedimentological%20signature%20which%2C%20albeit%20minor%2C%20might%20propagate%20into%20the%20depositional%20architecture%20of%20the%20platform%20when%20scaled%20over%20many%20storms%20through%20geological%20time.%20This%20work%20informs%20on%20the%20role%20of%20uniformitarianism%20versus%20catastrophism%20on%20carbonate%20sedimentation%20and%20casts%20doubt%20on%20geological%20interpretations%20of%20coarse-grained%20storm%20deposits%20%28tempestites%29%20atop%20shallow-water%20platforms.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212%5C%2F2022%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1111%5C%2Fsed.13020%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220037-0746%2C%201365-3091%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fonlinelibrary.wiley.com%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2F10.1111%5C%2Fsed.13020%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222022-11-23T06%3A48%3A04Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22PBV3FWIZ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Duquesne%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222021%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BDuquesne%2C%20F.%2C%20Vallaeys%2C%20V.%2C%20Vidaurre%2C%20P.%20J.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Hanert%2C%20E.%20%282021%29.%20A%20coupled%20ecohydrodynamic%20model%20to%20predict%20algal%20blooms%20in%20Lake%20Titicaca.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BEcological%20Modelling%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B440%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20109418.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.ecolmodel.2020.109418%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.ecolmodel.2020.109418%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22A%20coupled%20ecohydrodynamic%20model%20to%20predict%20algal%20blooms%20in%20Lake%20Titicaca%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Fran%5Cu00e7ois%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Duquesne%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Valentin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vallaeys%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Prem%20Jai%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vidaurre%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Emmanuel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hanert%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Lake%20Titicaca%20is%20home%20to%20a%20unique%20high-altitude%20ecosystem%20that%20is%20suffering%20from%20increasing%20anthropogenic%20pressures.%20It%20experienced%20its%20first%20major%20algal%20bloom%20in%20March%5Cu2013April%202015%20that%20had%20devastating%20consequences%20in%20the%20southern%20shallow%20lake%20basin.%20Such%20events%20are%20expected%20to%20intensify%20in%20the%20future%20and%20call%20for%20a%20more%20active%20and%20quantitative%20management%20of%20the%20lake%20and%20its%20watershed.%20In%20this%20paper%20we%20describe%20a%20coupled%20ecohydrodynamic%20model%20to%20predict%20the%20lake%5Cu2019s%20water%20quality%20and%2C%20more%20particularly%2C%20the%20risk%20of%20harmful%20algal%20blooms.%20We%20have%20coupled%20a%20nitrogen-phytoplankton-zooplankton-detritus%20%28NPZD%29%20ecosystem%20model%20to%20the%20unstructured-mesh%203D%20hydrodynamic%20model%20SLIM.%20Our%20high-resolution%20multi-scale%20model%20explicitly%20represents%20the%20exchanges%20between%20the%20two%20basins%20composing%20the%20lake%2C%20through%20the%20narrow%20Strait%20of%20Tiquina.%20This%20allowed%20us%20to%20study%20the%20biophysical%20processes%20driving%20the%20entire%20lake%20over%20the%20period%20of%20January%202014%20to%20May%202015.%20The%20model%20has%20been%20validated%20against%20temperature%20profiles%20at%20several%20locations%20throughout%20the%20lake.%20It%20correctly%20reproduces%20the%20seasonal%20temperature%20variations%20that%20drive%20the%20lake%20stratification%20and%20impact%20the%20vertical%20distributions%20of%20phytoplankton.%20Our%20model%20was%20able%20to%20replicate%20the%20space%5Cu2013time%20dynamics%20of%20the%20March%5Cu2013April%202015%20algal%20bloom%20similarly%20to%20what%20was%20observed%20on%20satellite%20imagery.%20We%20believe%20that%20our%20multiscale%20ecohydrodynamic%20model%20is%20a%20promising%20tool%20to%20complement%20field%20observations%20and%20hence%20support%20water%20management%20in%20the%20lake%20and%20its%20watershed.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2201%5C%2F2021%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.ecolmodel.2020.109418%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2203043800%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0304380020304750%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-12-29T06%3A27%3A02Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%225JI85ESB%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22lastModifiedByUser%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A5103066%2C%22username%22%3A%22ehanert%22%2C%22name%22%3A%22%22%2C%22links%22%3A%7B%22alternate%22%3A%7B%22href%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.zotero.org%5C%2Fehanert%22%2C%22type%22%3A%22text%5C%2Fhtml%22%7D%7D%7D%2C%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Pham%20Van%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222016%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A3%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPham%20Van%2C%20C.%2C%20Gourgue%2C%20O.%2C%20Sassi%2C%20M.%2C%20Hoitink%2C%20A.%20J.%20F.%2C%20Deleersnijder%2C%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Soares-Fraz%26%23xE3%3Bo%2C%20S.%20%282016%29.%20Modelling%20fine-grained%20sediment%20transport%20in%20the%20Mahakam%20land%26%23x2013%3Bsea%20continuum%2C%20Indonesia.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BJournal%20of%20Hydro-Environment%20Research%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B13%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20103%26%23x2013%3B120.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jher.2015.04.005%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jher.2015.04.005%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Modelling%20fine-grained%20sediment%20transport%20in%20the%20Mahakam%20land%5Cu2013sea%20continuum%2C%20Indonesia%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Chien%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pham%20Van%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Olivier%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gourgue%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Maximiliano%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sassi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.J.F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hoitink%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eric%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deleersnijder%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sandra%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Soares-Fraz%5Cu00e3o%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212%5C%2F2016%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.jher.2015.04.005%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2215706443%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS157064431500043X%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222023-03-06T09%3A30%3A32Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22DIJTQIIB%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Naithani%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222016%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BNaithani%2C%20J.%2C%20de%20Brye%2C%20B.%2C%20Buyze%2C%20E.%2C%20Vyverman%2C%20W.%2C%20Legat%2C%20V.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Deleersnijder%2C%20E.%20%282016%29.%20An%20ecological%20model%20for%20the%20Scheldt%20estuary%20and%20tidal%20rivers%20ecosystem%3A%20spatial%20and%20temporal%20variability%20of%20plankton.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BHydrobiologia%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B775%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%281%29%2C%2051%26%23x2013%3B67.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs10750-016-2710-1%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs10750-016-2710-1%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22An%20ecological%20model%20for%20the%20Scheldt%20estuary%20and%20tidal%20rivers%20ecosystem%3A%20spatial%20and%20temporal%20variability%20of%20plankton%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Naithani%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brye%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Buyze%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Vyverman%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Legat%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deleersnijder%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%227%5C%2F2016%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1007%5C%2Fs10750-016-2710-1%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220018-8158%2C%201573-5117%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flink.springer.com%5C%2F10.1007%5C%2Fs10750-016-2710-1%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222018-10-21T09%3A55%3A21Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22W9LQCTJP%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Delandmeter%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222015%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BDelandmeter%2C%20P.%2C%20Lewis%2C%20S.%20E.%2C%20Lambrechts%2C%20J.%2C%20Deleersnijder%2C%20E.%2C%20Legat%2C%20V.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Wolanski%2C%20E.%20%282015%29.%20The%20transport%20and%20fate%20of%20riverine%20fine%20sediment%20exported%20to%20a%20semi-open%20system.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BEstuarine%2C%20Coastal%20and%20Shelf%20Science%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B167%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20336%26%23x2013%3B346.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.ecss.2015.10.011%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.ecss.2015.10.011%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22The%20transport%20and%20fate%20of%20riverine%20fine%20sediment%20exported%20to%20a%20semi-open%20system%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Philippe%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Delandmeter%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Stephen%20E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lewis%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jonathan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lambrechts%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eric%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deleersnijder%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Vincent%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Legat%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eric%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wolanski%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Understanding%20the%20transport%20and%20fate%20of%20suspended%20sediment%20exported%20by%20rivers%20is%20crucial%20for%20the%20management%20of%20sensitive%20marine%20ecosystems.%20Sediment%20transport%20and%20fate%20can%20vary%20considerably%20depending%20on%20the%20geophysical%20characteristics%20of%20the%20coastal%20environment.%20Fine%20sediment%20transport%20was%20studied%20in%20a%20setting%20in%20between%20%5Cu201copen%5Cu201d%20%28uninterrupted%20coasts%29%20and%20%5Cu201csemi-enclosed%5Cu201d%20%28bays%29%20coastal%20systems%2C%20namely%20a%20%5Cu201csemi-open%5Cu201d%20system%20of%20shallow%20coastal%20water%20with%20long%20%28~20%20km%29%20stretches%20of%20open%20coasts%20separated%20by%20capes%20and%20headlands.%20The%20case%20study%20was%20the%20large%2C%20seasonal%2C%20Burdekin%20River%20that%20discharges%20to%20a%20wide%20continental%20shelf%20containing%20headlands%20and%20shallow%20embayments%20adjacent%20to%20the%20Great%20Barrier%20Reef%2C%20Australia.%20A%20new%20three-dimensional%20%5Cufb01ne%20sediment%20module%20for%20the%20unstructured-mesh%20SLIM%203D%20hydrodynamic%20model%20was%20developed.%20The%20model%20was%20successfully%20validated%20against%20available%20%5Cufb01eld%20data.%20The%20results%20were%20compared%20to%20previous%20studies%20on%20the%20Burdekin%20River%20sediment%20transport%20and%20differences%20were%20analysed.%20Wind%20direction%20and%20speed%20during%20river%20%5Cufb02oods%20largely%20control%20the%20dynamics%20and%20the%20fate%20of%20the%20%5Cufb01ne%20sediment.%20Most%20%2867%25%20for%202007%29%20of%20the%20riverine%20%5Cufb01ne%20sediment%20load%20is%20deposited%20near%20the%20river%20mouth%3B%20the%20remaining%20sediment%20is%20transported%20further%20a%5Cufb01eld%20in%20a%20riverine%20freshwater%20plume%3B%20that%20sediment%20can%20reach%20sensitive%20marine%20ecosystems%20and%20should%20be%20a%20priority%20for%20management.%20During%20the%20rest%20of%20the%20year%2C%20when%20the%20river%20%5Cufb02ow%20has%20ceased%2C%20wind-driven%20resuspension%20events%20redistribute%20the%20deposited%20sediment%20within%20embayments%20but%20generate%20negligible%20longshore%20transport.%20This%20study%20suggests%20that%20semi-open%20systems%20trap%20most%20of%20the%20riverine%20%5Cufb01ne%20sediment%2C%20somewhat%20like%20semi-enclosed%20systems.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212%5C%2F2015%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.ecss.2015.10.011%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2202727714%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0272771415301013%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222018-10-21T10%3A09%3A08Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%222IC3I784%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22de%20Brauwere%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222014%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3Bde%20Brauwere%2C%20A.%2C%20Gourgue%2C%20O.%2C%20de%20Brye%2C%20B.%2C%20Servais%2C%20P.%2C%20Ouattara%2C%20N.%20K.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Deleersnijder%2C%20E.%20%282014%29.%20Integrated%20modelling%20of%20faecal%20contamination%20in%20a%20densely%20populated%20river%26%23x2013%3Bsea%20continuum%20%28Scheldt%20River%20and%20Estuary%29.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BScience%20of%20The%20Total%20Environment%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B468%26%23x2013%3B469%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%2031%26%23x2013%3B45.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.scitotenv.2013.08.019%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.scitotenv.2013.08.019%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Integrated%20modelling%20of%20faecal%20contamination%20in%20a%20densely%20populated%20river%5Cu2013sea%20continuum%20%28Scheldt%20River%20and%20Estuary%29%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anouk%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brauwere%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Olivier%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gourgue%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Benjamin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brye%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Pierre%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Servais%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Nouho%20Koffi%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ouattara%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eric%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deleersnijder%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22In%20order%20to%20simulate%20the%20long-term%20%28months%5Cu2013years%29%20median%20Escherichia%20coli%20distributions%20and%20variations%20in%20the%20tidal%20Scheldt%20River%20and%20Estuary%2C%20a%20dedicated%20module%20was%20developed%20for%20the%20Second-generation%20Louvain-la-Neuve%20Iceocean%20Model%20%28SLIM%2C%20www.climate.be%5C%2Fslim%29.%20The%20resulting%20model%20%28SLIM-EC2%29%20presents%20two%20speci%5Cufb01c%20and%20new%20features%20compared%20to%20the%20older%20SLIM-EC%20model%20version.%20The%20%5Cufb01rst%20is%20that%20the%20E.%20coli%20concentrations%20in%20the%20river%20are%20split%20in%20three%20fractions%3A%20the%20free%20E.%20coli%20in%20the%20water%20column%2C%20the%20ones%20attached%20to%20suspended%20solids%20and%20those%20present%20in%20the%20bottom%20sediments%2C%20each%20with%20their%20own%20transport%2C%20decay%20and%20settling%5Cu2013resuspension%20dynamics.%20The%20bacteria%20attached%20to%20particles%20can%20settle%20and%20survive%20on%20the%20bottom%2C%20where%20they%20can%20be%20brought%20back%20in%20the%20water%20column%20during%20resuspension%20events.%20The%20second%20new%20feature%20of%20the%20model%20is%20that%20it%20is%20coupled%20to%20the%20catchment%20model%20SENEQUE-EC%2C%20which%20thus%20provides%20upstream%20boundary%20conditions%20to%20SLIM-EC2.%20The%20result%20is%20an%20integrated%20and%20multi-scale%20model%20of%20the%20whole%20Scheldt%20drainage%20network%20from%20its%20source%20down%20to%20the%20Belgian%5C%2FDutch%20coastal%20zone.%20This%20new%20model%20reproduces%20the%20long-term%20median%20E.%20coli%20concentration%20along%20the%20Scheldt%20River%20and%20Estuary.%20An%20extensive%20sensitivity%20study%20is%20performed%20demonstrating%20the%20relative%20robustness%20of%20the%20model%20with%20respect%20to%20the%20chosen%20parameterisations.%20In%20addition%20to%20reproducing%20the%20observed%20E.%20coli%20concentrations%20in%202007%5Cu20132008%20at%20various%20stations%2C%20two%20extreme%20wastewater%20management%20scenarios%20were%20considered.%20Overall%2C%20there%20is%20no%20doubt%20that%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary%20acts%20as%20a%20cleaning%20%5Cufb01lter%20of%20faecal%20contamination%20originating%20from%20large%20Belgian%20cities.%20As%20a%20result%2C%20at%20the%20mouth%20of%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary%20E.%20coli%20concentration%20is%20negligible%20in%20all%20investigated%20conditions.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2201%5C%2F2014%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.scitotenv.2013.08.019%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2200489697%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0048969713009339%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222018-10-21T09%3A49%3A37Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22XI2LFZYN%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Gourgue%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222013%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BGourgue%2C%20O.%2C%20Baeyens%2C%20W.%2C%20Chen%2C%20M.%20S.%2C%20de%20Brauwere%2C%20A.%2C%20de%20Brye%2C%20B.%2C%20Deleersnijder%2C%20E.%2C%20Elskens%2C%20M.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Legat%2C%20V.%20%282013%29.%20A%20depth-averaged%20two-dimensional%20sediment%20transport%20model%20for%20environmental%20studies%20in%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary%20and%20tidal%20river%20network.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BJournal%20of%20Marine%20Systems%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B128%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%2027%26%23x2013%3B39.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jmarsys.2013.03.014%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jmarsys.2013.03.014%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22A%20depth-averaged%20two-dimensional%20sediment%20transport%20model%20for%20environmental%20studies%20in%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary%20and%20tidal%20river%20network%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22O.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gourgue%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22W.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Baeyens%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Chen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brauwere%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brye%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deleersnijder%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Elskens%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22V.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Legat%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22This%20paper%20presents%20the%20sediment%20module%20designed%20for%20the%20two-dimensional%20depth-averaged%20and%20onedimensional%20section-averaged%20components%20of%20the%20%5Cufb01nite-element%20model%20SLIM%20%28Second-generation%20Louvainla-Neuve%20Ice-ocean%20Model%29%20in%20the%20framework%20of%20its%20application%20to%20the%20tidal%20part%20of%20the%20Scheldt%20Basin.%20This%20sediment%20transport%20module%20focuses%20on%20%5Cufb01ne-grained%2C%20cohesive%20sediments.%20It%20is%20a%20necessary%20tool%20to%20undertake%20environmental%20biogeochemical%20studies%2C%20in%20which%20%5Cufb01ne%20sediment%20dynamics%20play%20a%20crucial%20role.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2212%5C%2F2013%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.jmarsys.2013.03.014%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2209247963%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0924796313000833%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222018-10-21T11%3A11%3A43Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22D54SM3PI%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22de%20Brye%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222012%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3Bde%20Brye%2C%20B.%2C%20de%20Brauwere%2C%20A.%2C%20Gourgue%2C%20O.%2C%20Delhez%2C%20E.%20J.%20M.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Deleersnijder%2C%20E.%20%282012%29.%20Water%20renewal%20timescales%20in%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BJournal%20of%20Marine%20Systems%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B94%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%2074%26%23x2013%3B86.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jmarsys.2011.10.013%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jmarsys.2011.10.013%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Water%20renewal%20timescales%20in%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Benjamin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brye%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anouk%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brauwere%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Olivier%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gourgue%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eric%20J.M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Delhez%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eric%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deleersnijder%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Using%20the%20concepts%20of%20the%20Constituent-oriented%20Age%20and%20Residence%20time%20Theory%20%28CART%29%2C%20we%20compute%20timescales%20related%20to%20the%20water%20renewal%20in%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary%20%28The%20Netherlands%5C%2FBelgium%29.%20Three%20different%20timescales%20are%20used%20to%20better%20understand%20and%20characterize%20the%20dynamics%20of%20the%20estuary%3A%20the%20age%20of%20the%20renewing%20water%2C%20the%20residence%20time%20and%20the%20exposure%20time.%20The%20residence%20time%20is%20the%20time%20taken%20by%20a%20water%20parcel%20to%20leave%20the%20estuary%20for%20the%20%5Cufb01rst%20time%20while%20the%20exposure%20time%20is%20the%20total%20time%20spent%20by%20a%20water%20parcel%20in%20the%20estuary%20including%20re-entries.%20The%20age%20of%20a%20renewing%20water%20parcel%20is%20de%5Cufb01ned%20as%20the%20time%20elapsed%20since%20it%20entered%20the%20estuary.%20The%20renewing%20water%20was%20split%20into%20three%20types%3A%20the%20water%20originating%20from%20the%20sea%2C%20the%20water%20originating%20from%20the%20upstream%20fresh%20tidal%20rivers%20and%20the%20water%20originating%20from%20the%20different%20canals%20and%20docks%20connected%20to%20the%20estuary.%20Every%20timescale%20is%20computed%20at%20any%20time%20and%20position%20by%20means%20of%20the%20%5Cufb01nite-element%2C%20unstructured-mesh%20model%20SLIM.%20This%20results%20in%20movies%20of%20the%20timescale%20%5Cufb01elds%20%28shown%20as%20Supplementary%20material%29%2C%20allowing%20a%20detailed%20analysis%20of%20their%20spatial%20and%20temporal%20variabilities.%20The%20effect%20of%20the%20M2%20tide%20and%20the%20discharge%20regime%20%28winter%2C%20summer%20or%20average%20situation%29%20on%20the%20timescales%20is%20also%20investigated.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%226%5C%2F2012%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.jmarsys.2011.10.013%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2209247963%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0924796311002545%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222018-10-21T09%3A50%3A04Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%223THJ7UHX%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22de%20Brauwere%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222011%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3Bde%20Brauwere%2C%20A.%2C%20de%20Brye%2C%20B.%2C%20Servais%2C%20P.%2C%20Passerat%2C%20J.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Deleersnijder%2C%20E.%20%282011%29.%20Modelling%20Escherichia%20coli%20concentrations%20in%20the%20tidal%20Scheldt%20river%20and%20estuary.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BWater%20Research%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B45%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%289%29%2C%202724%26%23x2013%3B2738.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.watres.2011.02.003%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.watres.2011.02.003%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Modelling%20Escherichia%20coli%20concentrations%20in%20the%20tidal%20Scheldt%20river%20and%20estuary%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anouk%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brauwere%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Benjamin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brye%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Pierre%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Servais%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Julien%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Passerat%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eric%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deleersnijder%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Recent%20observations%20in%20the%20tidal%20Scheldt%20River%20and%20Estuary%20revealed%20a%20poor%20microbiological%20water%20quality%20and%20substantial%20variability%20of%20this%20quality%20which%20can%20hardly%20be%20assigned%20to%20a%20single%20factor.%20To%20assess%20the%20importance%20of%20tides%2C%20river%20discharge%2C%20point%20sources%2C%20upstream%20concentrations%2C%20mortality%20and%20settling%20a%20new%20model%20%28SLIM-EC%29%20was%20built.%20This%20model%20was%20%5Cufb01rst%20validated%20by%20comparison%20with%20the%20available%20%5Cufb01eld%20measurements%20of%20Escherichia%20coli%20%28E.%20coli%2C%20a%20common%20fecal%20bacterial%20indicator%29%20concentrations.%20The%20model%20simulations%20agreed%20well%20with%20the%20observations%2C%20and%20in%20particular%20were%20able%20to%20reproduce%20the%20observed%20longterm%20median%20concentrations%20and%20variability.%20Next%2C%20the%20model%20was%20used%20to%20perform%20sensitivity%20runs%20in%20which%20one%20process%5C%2Fforcing%20was%20removed%20at%20a%20time.%20These%20simulations%20revealed%20that%20the%20tide%2C%20upstream%20concentrations%20and%20the%20mortality%20process%20are%20the%20primary%20factors%20controlling%20the%20long-term%20median%20E.%20coli%20concentrations%20and%20the%20observed%20variability.%20The%20tide%20is%20crucial%20to%20explain%20the%20increased%20concentrations%20upstream%20of%20important%20inputs%2C%20as%20well%20as%20a%20generally%20increased%20variability.%20Remarkably%2C%20the%20wastewater%20treatment%20plants%20discharging%20in%20the%20study%20domain%20do%20not%20seem%20to%20have%20a%20signi%5Cufb01cant%20impact.%20This%20is%20due%20to%20a%20dilution%20effect%2C%20and%20to%20the%20fact%20that%20the%20concentrations%20coming%20from%20upstream%20%28where%20large%20cities%20are%20located%29%20are%20high.%20Overall%2C%20the%20settling%20process%20as%20it%20is%20presently%20described%20in%20the%20model%20does%20not%20signi%5Cufb01cantly%20affect%20the%20simulated%20E.%20coli%20concentrations.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2204%5C%2F2011%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.watres.2011.02.003%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2200431354%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0043135411000480%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222018-10-21T09%3A49%3A20Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22GCWGKGAZ%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22de%20Brauwere%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222011%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3Bde%20Brauwere%2C%20A.%2C%20de%20Brye%2C%20B.%2C%20Blaise%2C%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Deleersnijder%2C%20E.%20%282011%29.%20Residence%20time%2C%20exposure%20time%20and%20connectivity%20in%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BJournal%20of%20Marine%20Systems%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B84%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%283%26%23x2013%3B4%29%2C%2085%26%23x2013%3B95.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jmarsys.2010.10.001%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.jmarsys.2010.10.001%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Residence%20time%2C%20exposure%20time%20and%20connectivity%20in%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anouk%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brauwere%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Benjamin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brye%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S%5Cu00e9bastien%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Blaise%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eric%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deleersnijder%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Residence%20times%20and%20exposure%20times%20are%20computed%20for%2013%20boxes%20in%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary%2C%20using%20the%20highresolution%20tracer-transport%20model%20SLIM.%20The%20concepts%20are%20clearly%20de%5Cufb01ned%20and%20related%20to%20how%20they%20should%20be%20computed.%20First%2C%20the%20timescale%20values%20are%20compared%20with%20results%20published%20previously%20that%20were%20obtained%20with%20a%20simple%20box%20model%2C%20and%20an%20unexpected%20difference%20is%20revealed.%20This%20may%20suggest%20that%20a%20high-resolution%20model%20is%20necessary%2C%20even%20for%20the%20computation%20of%20such%20integrated%20quantities%20as%20residence%20or%20exposure%20times.%20Secondly%2C%20the%20newly%20computed%20residence%20times%20are%20compared%20to%20the%20exposures%20times%20to%20illustrate%20their%20intrinsic%20differences.%20From%20this%20difference%2C%20it%20is%20possible%20to%20propose%20a%20return%20coef%5Cufb01cient%2C%20expressing%20the%20fraction%20of%20the%20exposure%20time%20that%20is%20due%20to%20%5Cu201creturning%20water%5Cu201d%2C%20i.e.%20water%20which%20has%20already%20left%20the%20estuary%20at%20least%20once.%20Finally%2C%20the%20estuarine%20exposure%20times%20are%20decomposed%20into%20the%20different%20box%20exposure%20times%2C%20resulting%20in%20a%20connectivity%20matrix.%20This%20matrix%20expresses%20how%20much%20time%20is%20spent%20in%20each%20of%20the%20estuarine%20subdomains%20during%20the%20water%20parcels%26%23039%3B%20journey%20through%20the%20estuary.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222%5C%2F2011%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.jmarsys.2010.10.001%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2209247963%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0924796310001715%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222018-10-21T09%3A49%3A12Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22DWYWX3MR%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Pham%20Van%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222011%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BPham%20Van%2C%20C.%2C%20Spinewine%2C%20B.%2C%20de%20Brye%2C%20B.%2C%20Soares-Fraz%26%23xE3%3Bo%2C%20S.%2C%20Deleersnijder%2C%20E.%2C%20Sassi%2C%20M.%20G.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Hoitink%2C%20A.%20J.%20F.%20%282011%29.%20Multiscale%20modeling%20of%20a%20tidal%20estuary%20with%20a%20finite-element%20shallow-water%20model%3A%20application%20to%20salinity%20intrusion%20into%20the%20Mahakam%20delta%20%28Indonesia%29.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BRiver%2C%20Coastal%20and%20Estuarine%20Morphodynamics%3A%20RCEM2011%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%201068%26%23x2013%3B1081.%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22conferencePaper%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Multiscale%20modeling%20of%20a%20tidal%20estuary%20with%20a%20finite-element%20shallow-water%20model%3A%20application%20to%20salinity%20intrusion%20into%20the%20Mahakam%20delta%20%28Indonesia%29%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Chien%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pham%20Van%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Benoit%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Spinewine%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22B.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brye%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Sandra%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Soares-Fraz%5Cu00e3o%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deleersnijder%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Maximiliano%20G%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Sassi%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.%20J.%20F.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hoitink%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222011%22%2C%22proceedingsTitle%22%3A%22River%2C%20Coastal%20and%20Estuarine%20Morphodynamics%3A%20RCEM2011%22%2C%22conferenceName%22%3A%22%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%22%22%2C%22ISBN%22%3A%22%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222023-03-06T09%3A30%3A40Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22FFZ47STS%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22K%5Cu00e4rn%5Cu00e4%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222010%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BK%26%23xE4%3Brn%26%23xE4%3B%2C%20T.%2C%20Deleersnijder%2C%20E.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20de%20Brauwere%2C%20A.%20%282010%29.%20Simple%20test%20cases%20for%20validating%20a%20finite%20element%20unstructured%20grid%20fecal%20bacteria%20transport%20model.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BApplied%20Mathematical%20Modelling%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B34%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2810%29%2C%203055%26%23x2013%3B3070.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.apm.2010.01.012%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.apm.2010.01.012%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Simple%20test%20cases%20for%20validating%20a%20finite%20element%20unstructured%20grid%20fecal%20bacteria%20transport%20model%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tuomas%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22K%5Cu00e4rn%5Cu00e4%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eric%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deleersnijder%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anouk%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brauwere%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22This%20paper%20presents%20analytical%20test%20cases%20for%20tracer%20advection%5Cu2013diffusion-decay%20problems.%20The%20test%20cases%20are%20used%20to%20validate%20a%20%5Cufb01nite%20element%2C%20unstructured%20grid%20fecal%20bacteria%20transport%20model.%20The%20test%20cases%20include%20the%20following%20domains%3A%20one-dimensional%20in%5Cufb01nitely%20long%20river%2C%20two-dimensional%20half%20plane%20and%20two-dimensional%20in%5Cufb01nitely%20long%20channel.%20In%20this%20work%20the%20bacteria%20are%20considered%20to%20enter%20the%20domain%20only%20through%20point%20sources.%20Analytical%20solutions%20are%20derived%20using%20either%20a%20Dirac%20delta%20function%20or%20a%20variable-width%20Gaussian%20function%20as%20a%20point%20source.%20Both%20analytical%20derivations%20and%20numerical%20simulations%20suggest%20that%20the%20error%20is%20maximised%20at%20the%20source.%20We%20present%20formulae%20for%20estimating%20the%20error%20caused%20by%20replacing%20a%20Dirac%20source%20with%20a%20Gaussian%20function%20in%20the%20numerical%20model.%20Furthermore%2C%20numerical%20simulations%20suggest%20that%20the%20best%20approximation%20for%20a%20Dirac%20source%20is%20a%20Gaussian%20whose%20width%20parameter%20is%20one%20third%20of%20the%20local%20mesh%20size.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2210%5C%2F2010%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.apm.2010.01.012%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220307904X%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0307904X10000430%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222018-10-21T09%3A53%3A56Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22RVTR6QGI%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Lambrechts%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222010%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BLambrechts%2C%20J.%2C%20Humphrey%2C%20C.%2C%20McKinna%2C%20L.%2C%20Gourge%2C%20O.%2C%20Fabricius%2C%20K.%20E.%2C%20Mehta%2C%20A.%20J.%2C%20Lewis%2C%20S.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Wolanski%2C%20E.%20%282010%29.%20Importance%20of%20wave-induced%20bed%20liquefaction%20in%20the%20fine%20sediment%20budget%20of%20Cleveland%20Bay%2C%20Great%20Barrier%20Reef.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BEstuarine%2C%20Coastal%20and%20Shelf%20Science%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B89%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%282%29%2C%20154%26%23x2013%3B162.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.ecss.2010.06.009%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.ecss.2010.06.009%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Importance%20of%20wave-induced%20bed%20liquefaction%20in%20the%20fine%20sediment%20budget%20of%20Cleveland%20Bay%2C%20Great%20Barrier%20Reef%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lambrechts%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22C.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Humphrey%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22L.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22McKinna%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22O.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gourge%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22K.E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Fabricius%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22A.J.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Mehta%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22S.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lewis%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22E.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Wolanski%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Data%20from%20a%20three-year%20long%20%5Cufb01eld%20study%20of%20%5Cufb01ne%20sediment%20dynamics%20in%20Cleveland%20Bay%20show%20that%20waveinduced%20liquefaction%20of%20the%20%5Cufb01ne%20sediment%20bed%20on%20the%20sea%5Cufb02oor%20in%20shallow%20water%20was%20the%20main%20process%20causing%20bed%20erosion%20under%20small%20waves%20during%20tradewinds%2C%20and%20that%20shear-induced%20erosion%20prevailed%20during%20cyclonic%20conditions.%20These%20data%20were%20used%20to%20verify%20a%20model%20of%20%5Cufb01ne%20sediment%20dynamics%20that%20calculates%20sediment%20resuspension%20by%20both%20excess%20shear%20stress%20and%20wave-induced%20liquefaction%20of%20the%20bed.%20For%20present%20land-use%20conditions%2C%20the%20amount%20of%20riverine%20sediments%20settling%20on%20the%20bay%20may%20exceed%20by%2050e75%25%20the%20amount%20of%20sediment%20exported%20from%20the%20bay.%20Sediment%20is%20thus%20accumulating%20in%20the%20bay%20on%20an%20annual%20basis%2C%20which%20in%20turn%20may%20degrade%20the%20fringing%20coral%20reefs.%20For%20those%20years%20when%20a%20tropical%20cyclone%20impacted%20the%20bay%20there%20may%20be%20a%20net%20sediment%20out%5Cufb02ow%20from%20the%20bay.%20During%20the%20dry%2C%20tradewind%20season%2C%20%5Cufb01ne%20sediment%20was%20progressively%20winnowed%20out%20of%20the%20shallow%2C%20reefal%20waters.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%229%5C%2F2010%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.ecss.2010.06.009%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2202727714%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0272771410002295%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222018-10-21T09%3A54%3A26Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22YH3BD43T%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22de%20Brauwere%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222009%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3Bde%20Brauwere%2C%20A.%2C%20De%20Ridder%2C%20F.%2C%20Gourgue%2C%20O.%2C%20Lambrechts%2C%20J.%2C%20Comblen%2C%20R.%2C%20Pintelon%2C%20R.%2C%20Passerat%2C%20J.%2C%20Servais%2C%20P.%2C%20Elskens%2C%20M.%2C%20Baeyens%2C%20W.%2C%20K%26%23xE4%3Brn%26%23xE4%3B%2C%20T.%2C%20de%20Brye%2C%20B.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Deleersnijder%2C%20E.%20%282009%29.%20Design%20of%20a%20sampling%20strategy%20to%20optimally%20calibrate%20a%20reactive%20transport%20model%3A%20Exploring%20the%20potential%20for%20Escherichia%20coli%20in%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BEnvironmental%20Modelling%20%26amp%3B%20Software%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B24%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%288%29%2C%20969%26%23x2013%3B981.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.envsoft.2009.02.004%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1016%5C%2Fj.envsoft.2009.02.004%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Design%20of%20a%20sampling%20strategy%20to%20optimally%20calibrate%20a%20reactive%20transport%20model%3A%20Exploring%20the%20potential%20for%20Escherichia%20coli%20in%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Anouk%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brauwere%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Fjo%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22De%20Ridder%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Olivier%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Gourgue%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jonathan%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lambrechts%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Richard%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Comblen%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rik%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Pintelon%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Julien%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Passerat%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Pierre%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Servais%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Marc%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Elskens%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Willy%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Baeyens%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Tuomas%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22K%5Cu00e4rn%5Cu00e4%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Benjamin%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22de%20Brye%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eric%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deleersnijder%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22For%20the%20calibration%20of%20any%20model%2C%20measurements%20are%20necessary.%20As%20measurements%20are%20expensive%2C%20it%20is%20of%20interest%20to%20determine%20beforehand%20which%20kind%20of%20samples%20will%20provide%20maximal%20information.%20Using%20a%20criterion%20related%20to%20the%20Fisher%20information%20matrix%20as%20a%20measure%20for%20information%20content%2C%20it%20is%20possible%20to%20design%20a%20sampling%20scheme%20that%20will%20enable%20the%20most%20precise%20parameter%20estimates.%20This%20approach%20was%20applied%20to%20a%20reactive%20transport%20model%20%28based%20on%20the%20Second-generation%20Louvain-la-Neuve%20Ice-ocean%20Model%2C%20SLIM%29%20of%20Escherichia%20coli%20concentrations%20in%20the%20Scheldt%20Estuary.%20As%20this%20estuary%20is%20highly%20in%5Cufb02uenced%20by%20the%20tide%2C%20it%20is%20expected%20that%20careful%20timing%20of%20the%20samples%20with%20respect%20to%20the%20tidal%20cycle%20can%20have%20an%20effect%20on%20the%20quality%20of%20the%20data.%20The%20timing%20and%20also%20the%20positioning%20of%20samples%20were%20optimised%20according%20to%20the%20proposed%20criterion.%20In%20the%20investigated%20case%20studies%20the%20precision%20of%20the%20estimated%20parameters%20could%20be%20improved%20by%20up%20to%20a%20factor%20of%20ten%2C%20con%5Cufb01rming%20the%20usefulness%20of%20this%20approach%20to%20maximize%20the%20amount%20of%20information%20that%20can%20be%20retrieved%20from%20a%20%5Cufb01xed%20number%20of%20samples.%20Precise%20parameter%20values%20will%20result%20in%20more%20reliable%20model%20simulations%2C%20which%20can%20be%20used%20for%20interpretation%2C%20or%20can%20in%20turn%20serve%20to%20plan%20subsequent%20sampling%20campaigns%20to%20further%20constrain%20the%20model%20parameters.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%228%5C%2F2009%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.envsoft.2009.02.004%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%2213648152%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Flinkinghub.elsevier.com%5C%2Fretrieve%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS136481520900036X%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222018-10-21T09%3A49%3A31Z%22%7D%7D%2C%7B%22key%22%3A%22AVEPBCBL%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A778265%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22White%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222008%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-bib-body%26quot%3B%20style%3D%26quot%3Bline-height%3A%202%3B%20padding-left%3A%201em%3B%20text-indent%3A-1em%3B%26quot%3B%26gt%3B%5Cn%20%20%26lt%3Bdiv%20class%3D%26quot%3Bcsl-entry%26quot%3B%26gt%3BWhite%2C%20L.%2C%20Legat%2C%20V.%2C%20%26amp%3B%20Deleersnijder%2C%20E.%20%282008%29.%20Tracer%20Conservation%20for%20Three-Dimensional%2C%20Finite-Element%2C%20Free-Surface%2C%20Ocean%20Modeling%20on%20Moving%20Prismatic%20Meshes.%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3BMonthly%20Weather%20Review%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%2C%20%26lt%3Bi%26gt%3B136%26lt%3B%5C%2Fi%26gt%3B%282%29%2C%20420%26%23x2013%3B442.%20%26lt%3Ba%20class%3D%26%23039%3Bzp-DOIURL%26%23039%3B%20href%3D%26%23039%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1175%5C%2F2007MWR2137.1%26%23039%3B%26gt%3Bhttps%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fdoi.org%5C%2F10.1175%5C%2F2007MWR2137.1%26lt%3B%5C%2Fa%26gt%3B%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%5Cn%26lt%3B%5C%2Fdiv%26gt%3B%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Tracer%20Conservation%20for%20Three-Dimensional%2C%20Finite-Element%2C%20Free-Surface%2C%20Ocean%20Modeling%20on%20Moving%20Prismatic%20Meshes%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Laurent%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22White%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Vincent%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Legat%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Eric%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Deleersnijder%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22Large-scale%20free-surface%20ocean%20models%20designed%20to%20run%20over%20climatic%20time%20scales%20are%20required%20to%20globally%20conserve%20the%20volume%20and%20any%20tracer%20up%20to%20machine%20precision.%20In%20addition%2C%20local%20consistency%20is%20critical%20and%20requires%20that%20the%20discrete%20tracer%20equation%20preserve%20constants%20in%20a%20closed%20domain%20and%20if%20there%20is%20no%20tracer%20source%20or%20sink.%20Local%20consistency%2C%20together%20with%20monotonicity%2C%20will%20ensure%20that%20no%20spurious%20tracer%20extrema%20occur.%20A%20three-dimensional%2C%20finite-element%2C%20shallow-water%20model%20is%20presented.%20The%20mesh%20is%20unstructured%20in%20the%20horizontal%2C%20extruded%20in%20the%20third%20dimension%2C%20and%20made%20up%20of%20multiple%20layers%20of%20prisms.%20In%20addition%2C%20the%20mesh%20is%20allowed%20to%20move%20in%20the%20vertical%20and%20adapts%20itself%20to%20the%20free-surface%20motions.%20It%20is%20shown%20that%20achieving%20consistency%20requires%20a%20discrete%20compatibility%20between%20the%20tracer%20and%20continuity%20equations.%20In%20addition%2C%20to%20ensure%20global%20tracer%20conservation%20in%20a%20consistent%20way%2C%20a%20discrete%20compatibility%20between%20the%20tracer%2C%20continuity%2C%20and%20free-surface%20elevation%20equations%20must%20be%20fulfilled.%20It%20is%20suggested%20that%20this%20compatibility%20constraint%2C%20together%20with%20the%20use%20of%20a%20numerically%20stable%20scheme%2C%20severely%20restricts%20the%20choice%20of%20usable%20finite-element%20spatial%20discretizations.%20A%20consistent%20and%20conservative%20time-stepping%20algorithm%20is%20described%20for%20which%20a%20unique%20time%20step%20is%20used.%20It%20is%20suggested%20that%20future%20research%20is%20needed%20in%20order%20to%20design%20a%20consistent%20and%20conservative%20split-explicit%20algorithm.%20Some%20illustrative%20test%20cases%20are%20presented%20in%20which%20the%20method%20is%20shown%20to%20satisfy%20all%20conservation%20properties.%20A%20few%20experiments%20in%20which%20consistency%20breaks%20down%20are%20carried%20out%2C%20and%20the%20consequences%20of%20this%20breakdown%20process%20are%20investigated.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%2202%5C%2F2008%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1175%5C%2F2007MWR2137.1%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220027-0644%2C%201520-0493%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fjournals.ametsoc.org%5C%2Fdoi%5C%2Fabs%5C%2F10.1175%5C%2F2007MWR2137.1%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22GJSQZPDC%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222018-10-21T09%3A58%3A28Z%22%7D%7D%5D%7D
Purkis, S. J., Oehlert, A. M., Dobbelaere, T., Hanert, E., & Harris, P. (Mitch). (2023). Always a White Christmas in the Bahamas: temperature and hydrodynamics localize winter mud production on Great Bahama Bank.
Journal of Sedimentary Research ,
93 (3), 145–160.
https://doi.org/10.2110/jsr.2022.066
Lopez‐Gamundi, C., Dobbelaere, T., Hanert, E., Harris, P. M., Eberli, G., & Purkis, S. J. (2022). Simulating sedimentation on the Great Bahama Bank – Sources, sinks and storms.
Sedimentology ,
69 (7), 2693–2714.
https://doi.org/10.1111/sed.13020
Duquesne, F., Vallaeys, V., Vidaurre, P. J., & Hanert, E. (2021). A coupled ecohydrodynamic model to predict algal blooms in Lake Titicaca.
Ecological Modelling ,
440 , 109418.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2020.109418
Pham Van, C., Gourgue, O., Sassi, M., Hoitink, A. J. F., Deleersnijder, E., & Soares-Frazão, S. (2016). Modelling fine-grained sediment transport in the Mahakam land–sea continuum, Indonesia.
Journal of Hydro-Environment Research ,
13 , 103–120.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2015.04.005
Naithani, J., de Brye, B., Buyze, E., Vyverman, W., Legat, V., & Deleersnijder, E. (2016). An ecological model for the Scheldt estuary and tidal rivers ecosystem: spatial and temporal variability of plankton.
Hydrobiologia ,
775 (1), 51–67.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2710-1
Delandmeter, P., Lewis, S. E., Lambrechts, J., Deleersnijder, E., Legat, V., & Wolanski, E. (2015). The transport and fate of riverine fine sediment exported to a semi-open system.
Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science ,
167 , 336–346.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2015.10.011
de Brauwere, A., Gourgue, O., de Brye, B., Servais, P., Ouattara, N. K., & Deleersnijder, E. (2014). Integrated modelling of faecal contamination in a densely populated river–sea continuum (Scheldt River and Estuary).
Science of The Total Environment ,
468–469 , 31–45.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.019
Gourgue, O., Baeyens, W., Chen, M. S., de Brauwere, A., de Brye, B., Deleersnijder, E., Elskens, M., & Legat, V. (2013). A depth-averaged two-dimensional sediment transport model for environmental studies in the Scheldt Estuary and tidal river network.
Journal of Marine Systems ,
128 , 27–39.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2013.03.014
de Brye, B., de Brauwere, A., Gourgue, O., Delhez, E. J. M., & Deleersnijder, E. (2012). Water renewal timescales in the Scheldt Estuary.
Journal of Marine Systems ,
94 , 74–86.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2011.10.013
de Brauwere, A., de Brye, B., Servais, P., Passerat, J., & Deleersnijder, E. (2011). Modelling Escherichia coli concentrations in the tidal Scheldt river and estuary.
Water Research ,
45 (9), 2724–2738.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.02.003
de Brauwere, A., de Brye, B., Blaise, S., & Deleersnijder, E. (2011). Residence time, exposure time and connectivity in the Scheldt Estuary.
Journal of Marine Systems ,
84 (3–4), 85–95.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2010.10.001
Pham Van, C., Spinewine, B., de Brye, B., Soares-Frazão, S., Deleersnijder, E., Sassi, M. G., & Hoitink, A. J. F. (2011). Multiscale modeling of a tidal estuary with a finite-element shallow-water model: application to salinity intrusion into the Mahakam delta (Indonesia). River, Coastal and Estuarine Morphodynamics: RCEM2011 , 1068–1081.
Kärnä, T., Deleersnijder, E., & de Brauwere, A. (2010). Simple test cases for validating a finite element unstructured grid fecal bacteria transport model.
Applied Mathematical Modelling ,
34 (10), 3055–3070.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2010.01.012
Lambrechts, J., Humphrey, C., McKinna, L., Gourge, O., Fabricius, K. E., Mehta, A. J., Lewis, S., & Wolanski, E. (2010). Importance of wave-induced bed liquefaction in the fine sediment budget of Cleveland Bay, Great Barrier Reef.
Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science ,
89 (2), 154–162.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2010.06.009
de Brauwere, A., De Ridder, F., Gourgue, O., Lambrechts, J., Comblen, R., Pintelon, R., Passerat, J., Servais, P., Elskens, M., Baeyens, W., Kärnä, T., de Brye, B., & Deleersnijder, E. (2009). Design of a sampling strategy to optimally calibrate a reactive transport model: Exploring the potential for Escherichia coli in the Scheldt Estuary.
Environmental Modelling & Software ,
24 (8), 969–981.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2009.02.004
White, L., Legat, V., & Deleersnijder, E. (2008). Tracer Conservation for Three-Dimensional, Finite-Element, Free-Surface, Ocean Modeling on Moving Prismatic Meshes.
Monthly Weather Review ,
136 (2), 420–442.
https://doi.org/10.1175/2007MWR2137.1